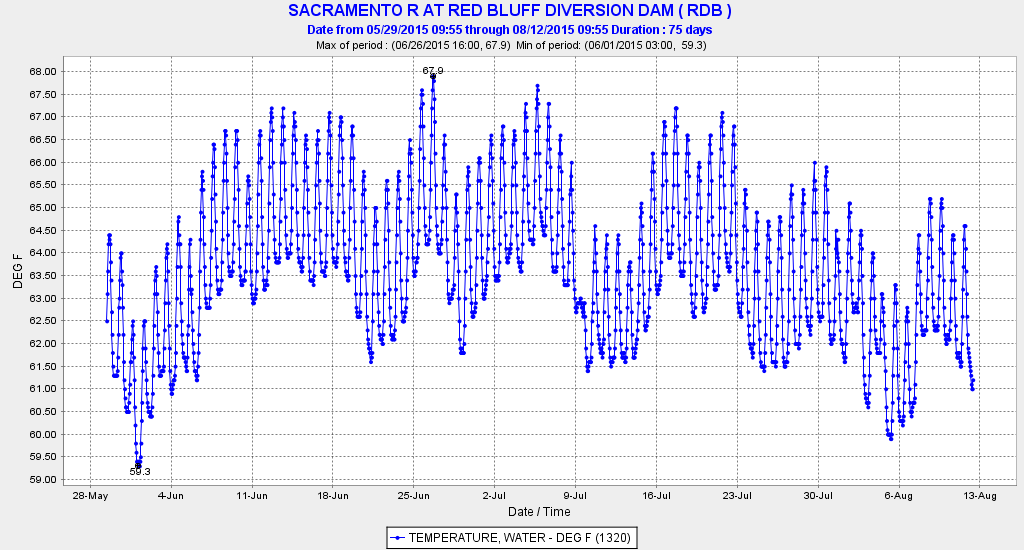
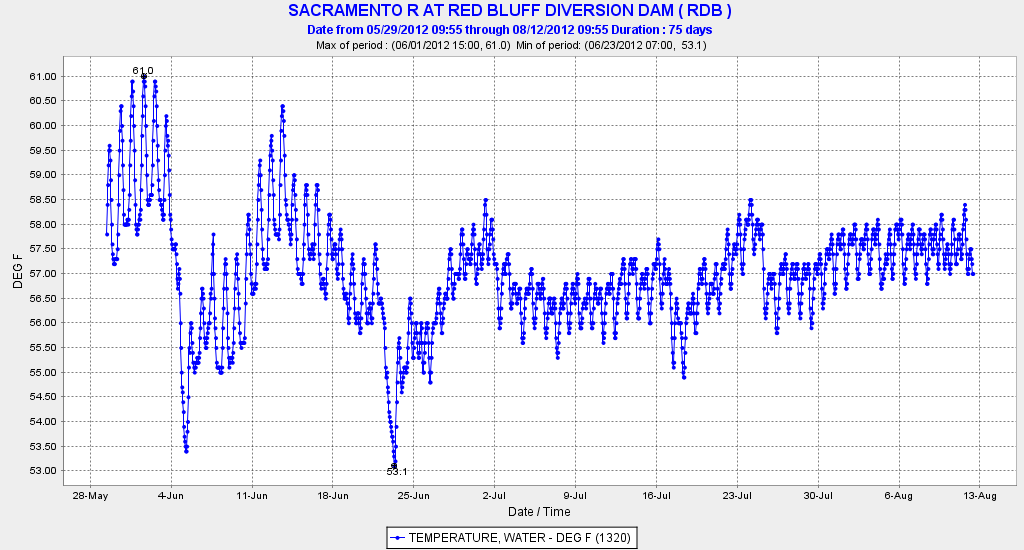
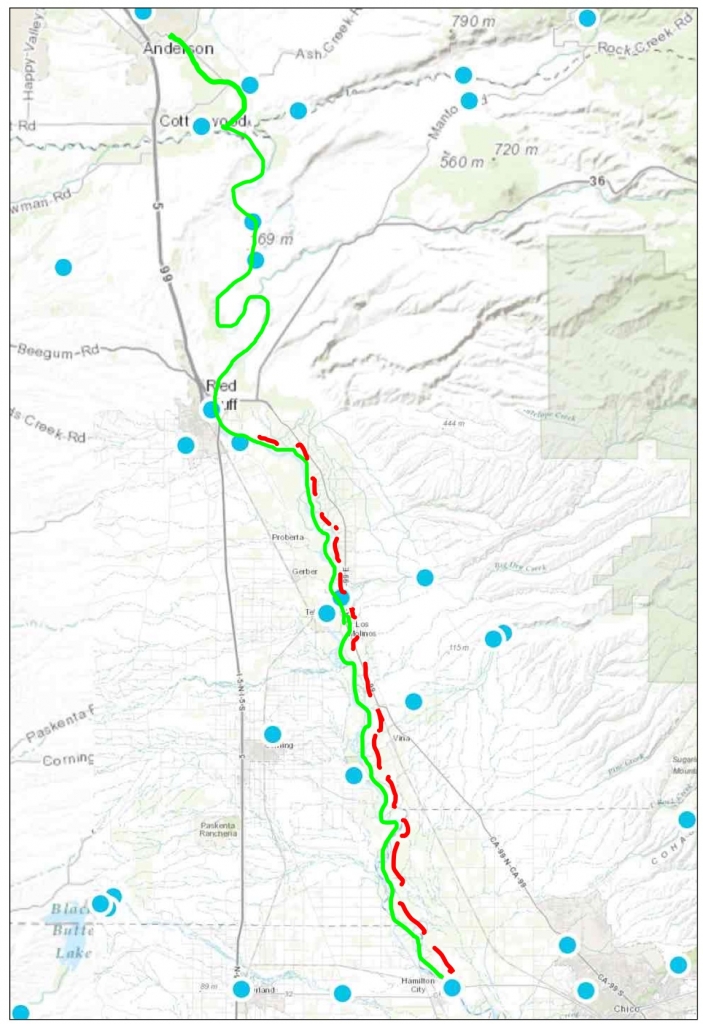
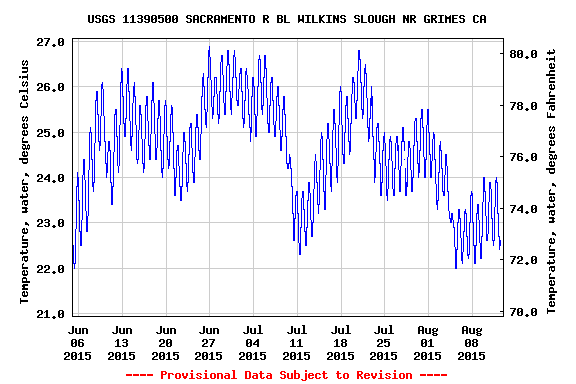
In a recent editorial, the Fresno Bee editorial board1 stated that restoring salmon near Fresno in the San Joaquin River below Friant Dam is a “fool’s errand.” The editorial referred to recent events near Shasta Dam on the Sacramento River: “This decimation (of Sacramento Winter Run salmon) has occurred despite the best efforts of federal officials to save salmon – and at the expense of irrigation water for farmers. Officials, in fact, sharply curtailed water flows out of Lake Shasta last spring in an attempt to keep sufficient cold water in the system to support the fish.” The editorial further stated: “If the Sacramento can’t sustain healthy salmon runs without crippling farmers, what are the prospects that the San Joaquin River – with less water and higher temperatures – can flow with spring-run salmon again? The editorial implies that it is a waste of time trying to save salmon, especially San Joaquin salmon, “at the expense of irrigation water for farmers”.
Well, the Fresno Bee’s editors are wrong. Both salmon populations can be restored. The feds’ efforts at Shasta were in fact not their best. Yes, most of the Winter Run Salmon died in 2015 as in 2014, but the salmon could have been saved (see our recent post).2 Farmers weren’t “crippled” by salmon: there was simply too little water to supply farmers, especially south of the Delta based on water right allocation priorities. No additional water could have been released from Trinity or Shasta without jeopardizing next year’s water supplies (or salmon). In both 2014 and 2015, the Sacramento River Settlement Contractors got most of their allocation (75% – over 1 MAF including water from Trinity Reservoir); at the end of 2015 in particular, many transferred water south of Delta. Again, this was hardly crippling. The Settlement Contractors could have and should have been allocated less. They would have survived. The salmon did not. The salmon died from mismanagement of the water supplies and hydropower system, and because the managing agencies deliberately allowed water temperatures to stay for months above the safe level for incubating eggs.
There is no reason healthy salmon runs cannot be sustained in both rivers. Most of the water released for salmon will still go to farmers.
Here is the best strategy for San Joaquin River salmon.
- Spring Run Salmon Only – There is a unique opportunity in this program to keep Fall Run and Spring Run apart to allow the native Spring Run to recover. Do not haul Fall Run salmon to the upper river or include Fall Run in the conservation hatchery.
- Conservation Hatchery – The San Joaquin needs a conservation hatchery to raise Spring Run salmon of an appropriate genetic stock for the San Joaquin. Such a facility is planned but so far it is only an “interim facility.”3 It is called the Salmon Conservation and Research Facility (SCARF).4 Its plan calls for using Feather hatchery spring run eggs. That is a problem – the hatchery must start with eggs from native Central Valley stocks (Deer, Mill and Butte creeks), not “summer run” hybrids from the Feather River. Yes, the San Joaquin is warmer, which is why having Feather “spring run” that migrate in May and June is not a wise choice. March-April is a better time for adult upstream migrations in the San Joaquin, which is the timing the Deer, Mill and Butte creek stocks can provide. The program review team recognizes this: “Moving forward, there is a program goal of reintroducing multiple stocks from more than one spring-running population available, but there are a lot of questions that need to be answered from a genetics standpoint, in order to make sure reproductive success and survivability of progeny is maximized using pedigree-based genetic marking techniques.”5 The draft EIR (p. 6-57) for the new hatchery argues against using eggs from Deer,Mill or Butte creeks as it poses a threat to the Deer, Mill and Butte creek populations: “Propagation of fish at the SCARF has the potential to unintentionally change the genetic composition of wild populations and subsequently contribute to reduced survival in natural environments if conservation stock stray into the Sacramento River basin and spawn with wild spring-run stocks. Additionally, conservation stock may stray into other tributaries of the San Joaquin River basin and interbreed with fall-run Chinook, which may interfere with existing wild and hatchery management actions and reduce genetic fitness of these fall-run populations.”6 I contend that using Feather “spring run” that are already “compromised” genetically would pose a greater threat to other Central Valley stocks. The technical review team seems to recognize this. The federal Salmon Recovery Plan has a goal of adding more stock diversity to the Central Valley salmon populations to reduce the threat of extinctions.
- Trap-and-Haul – The young salmon produced by the conservation hatchery or produced by wild spawning salmon near Fresno should be trapped and hauled to the Bay except in wet years when river flows are high and the lower river is connected. The present plan is to trap the young and transport them for release near the mouth of the Merced River. Most of these fish would not survive downstream passage through the lower San Joaquin and the Delta except in high flow wet years. The young fish should be “barged” in boats with live wells and recirculating river water to ensure they continue imprinting on the San Joaquin. This avoids many problems discussed in the Issue Paper on Delta effects.7
- Winter-Spring Pulse Flows in Wet Years – Young Spring Run would migrate downstream to the Bay and Delta from December to February as fry and fingerlings, and March and April as pre-smolts. Adults would migrate upstream in March and April. In wet years with substantial natural connection, river flows and water supply, supplemental reservoir releases could be made to improve migration survival. Such conditions may occur after or between storms, or simply to enhance storm flow peaks of less than adequate magnitude. Such added flows could be coordinated with Sacramento flows and Delta conditions. Delta conditions (Delta exports, Head of Old River Barrier, and Delta Cross Channel operations) could also be modified to help young San Joaquin salmon in wetter years when they would be passing through the Delta, and in all years when adults pass through the Delta.
As well as being a legal requirement and the correction of a grievous moral injustice, restoration of Spring Run salmon remains a viable goal for the San Joaquin River.
- http://www.fresnobee.com/opinion/editorials/article41954859.html ↩
- http://calsport.org/fisheriesblog/?p=511 ↩
- The Interim Facility is intended to operate as a conservation facility, differing from conventional hatcheries in that it is managed to maximize genetic diversity of its captive brood stock. ↩
- https://www.wildlife.ca.gov/Regions/4/San-Joaquin-River ↩
- http://www.westcoast.fisheries.noaa.gov/publications/Central_Valley /San%20Joaquin/genetics_sr_tech_mtnotes_07242014.pdf ↩
- https://nrm.dfg.ca.gov/FileHandler.ashx?DocumentID=73969&inline=1 ↩
- http://www.westcoast.fisheries.noaa.gov/publications/Central_Valley /San%20Joaquin/sjr_spring-run_issue_paper_2013-0723.pdf ↩